How to calculate EPR Targets for Battery Waste (Case Study)
In this article, through case studies, we explain the method to calculate the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) targets for Producers under the Battery Waste (Management) Rules, 2022.
1. Type of Batteries Covered Under EPR
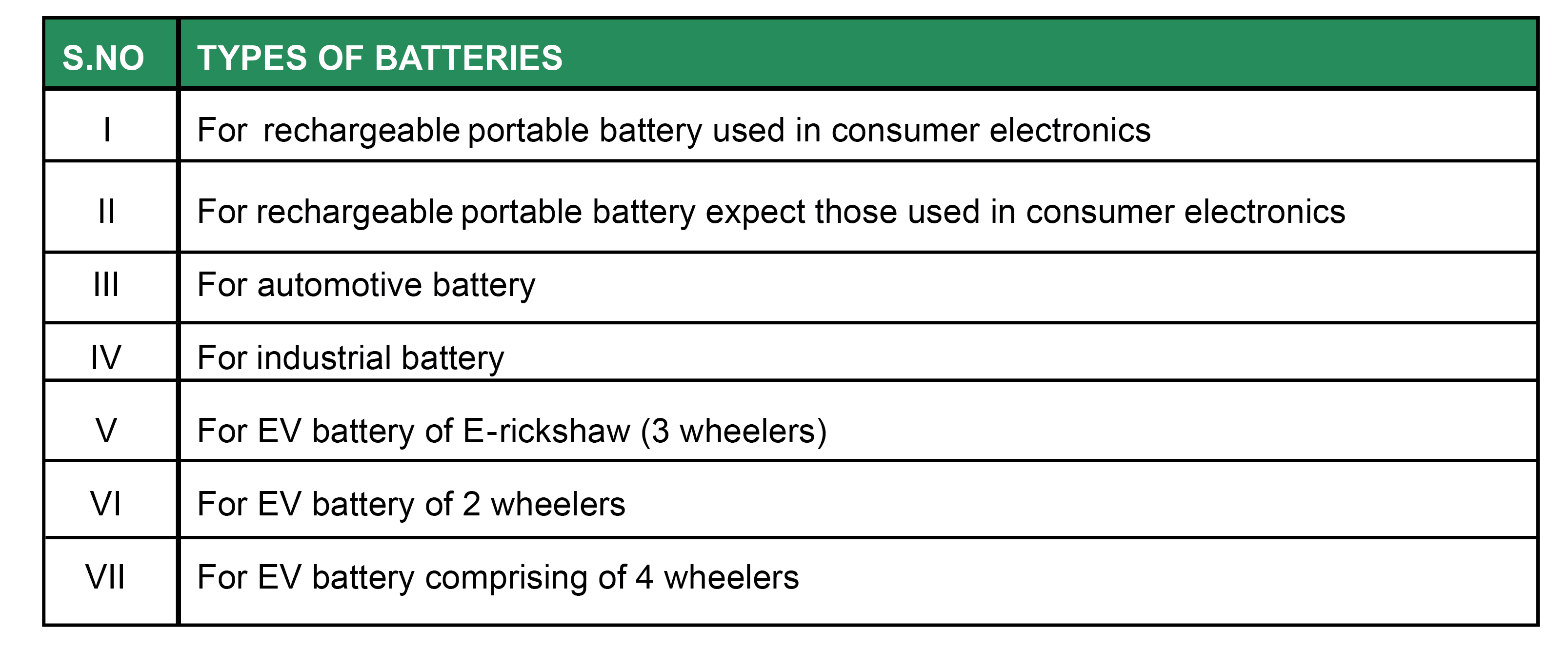
2. Targets for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
• Producers shall meet their EPR obligation through EPR certificates provided by the recyclers/ refurbishers on the CPCB’s online portal.
• There are year wise EPR targets as well as cumulative EPR target for the given compliance cycle. These targets are different for different type of batteries. The same is explained through a case study in the next section.
• The EPR target for recyclable portable batteries used in consumer electronics started in year 2022-23.
• The EPR target for automotive and industrial batteries started in year 2022-23.
• The EPR target for recyclable portable batteries used in non-consumer electronics starts in year 2025-26.
• The EPR target for EV batteries in E-Rickshaw (3 wheelers) starts in year 2024-25.
• The EPR target for EV batteries in two (2) wheeler vehicles starts in year 2026-27.
• The EPR target for EV batteries in four (4) wheeler vehicles starts in year 2029-30.
3. Case study- Calculation of EPR Targets
I) A Producer Selling Rechargeable Portable Battery Used in Consumer Electronics
Let’s take the case of a battery producer company “XYZ”. This company produces and sells rechargeable batteries used in consumer electronics. Company “XYZ” started its operation in Indian market in the year 2017-18.
The sales (by weight) made by “XYZ” in various years is given in table 1 below;
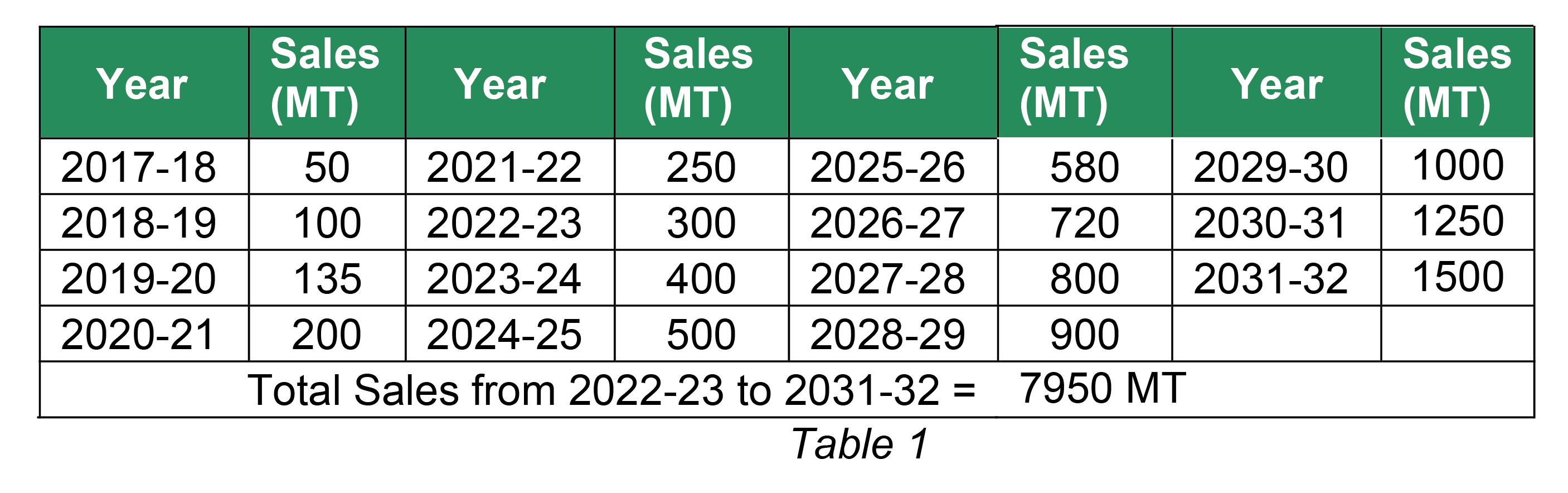
As per the clause (vi) of Schedule II of Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, the EPR liability of “XYZ” for the “rechargeable portable batteries used in consumer electronics” would be as given in table 2 below;

Total year wise EPR target fulfilled by “XYZ” = 2244.5 MT
The EPR target of complete 10 year CC (2022-23 to 2031-32) = 7950 MT
The balance EPR liability of ‘XYZ’ for the said CC = 7950 – 2244.5 = 5705.5 MT
However, as per the clause (vi) of Schedule II of the said rules, 60% of the average quantity of the battery sold per year during the compliance cycle (2022-23 to 2031-32) could be carried forward to the next compliance cycle (2032-33 to 2041-42)
Average quantity of battery sold /year during 2022-23 to 2031-32 = 7950/10 = 795 MT
Hence, carry forward quantity = 60% * 795 = 477 MT
Therefore, the balance mandatory EPR liability of company ‘XYZ’ during the compliance cycle of 2022-23 to 2031-32 = 5705.5 – 384 = 5228.5 MT
II) A Producer Selling EV Battery for E-Rickshaw and 2 Wheeler Vehicles
Let’s take the case of a battery producer company “PQR”. This company produces and sells EV batteries for 2 wheeler and 3 wheeler vehicles. Company “PQR” started its operation in Indian market in the year 2020-21.
Sales (by weight) of “PQR” for 3 (three) wheeler EV batteries is as given in table 3 below;
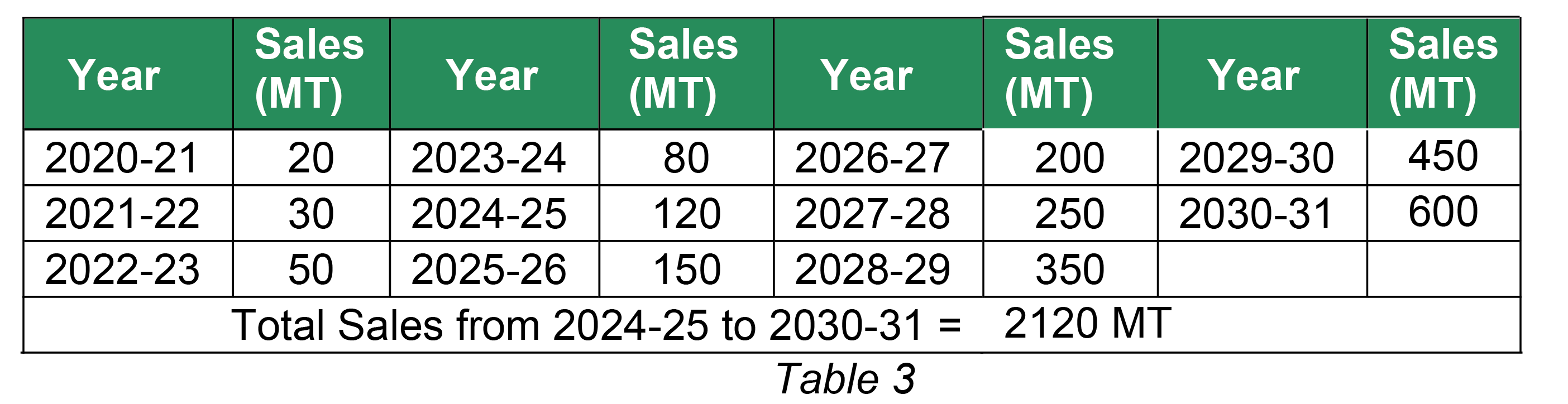
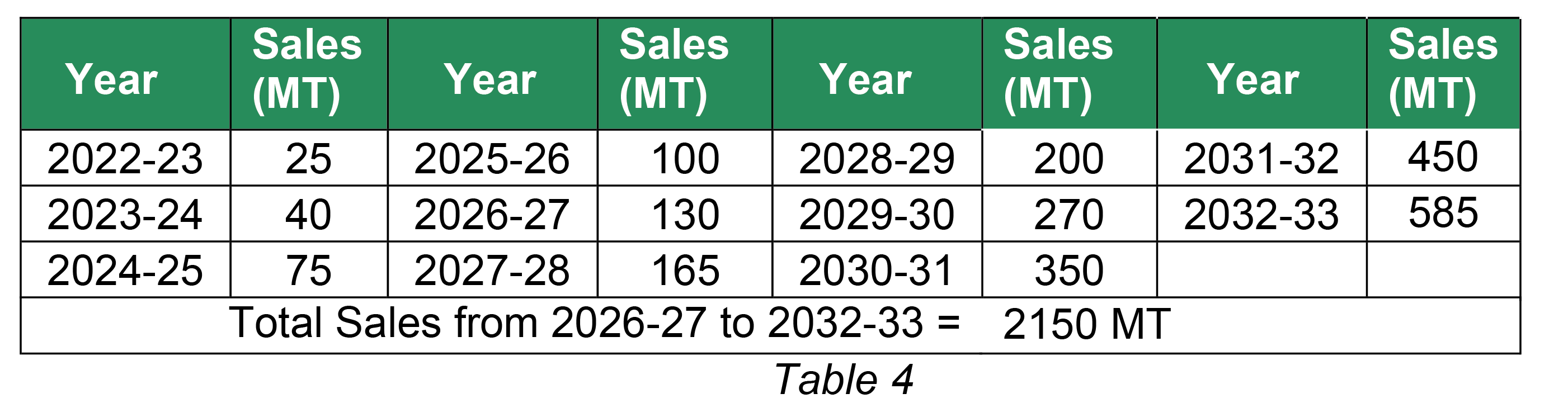
Sales (by weight) of “PQR” for 2 (two) wheeler EV batteries is as given in table 4 below;
(a) As per clause (x) of Schedule II of Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, the EPR liability of “PQR” for ‘EV battery for 3 wheelers’ would be as given in table 5 below;

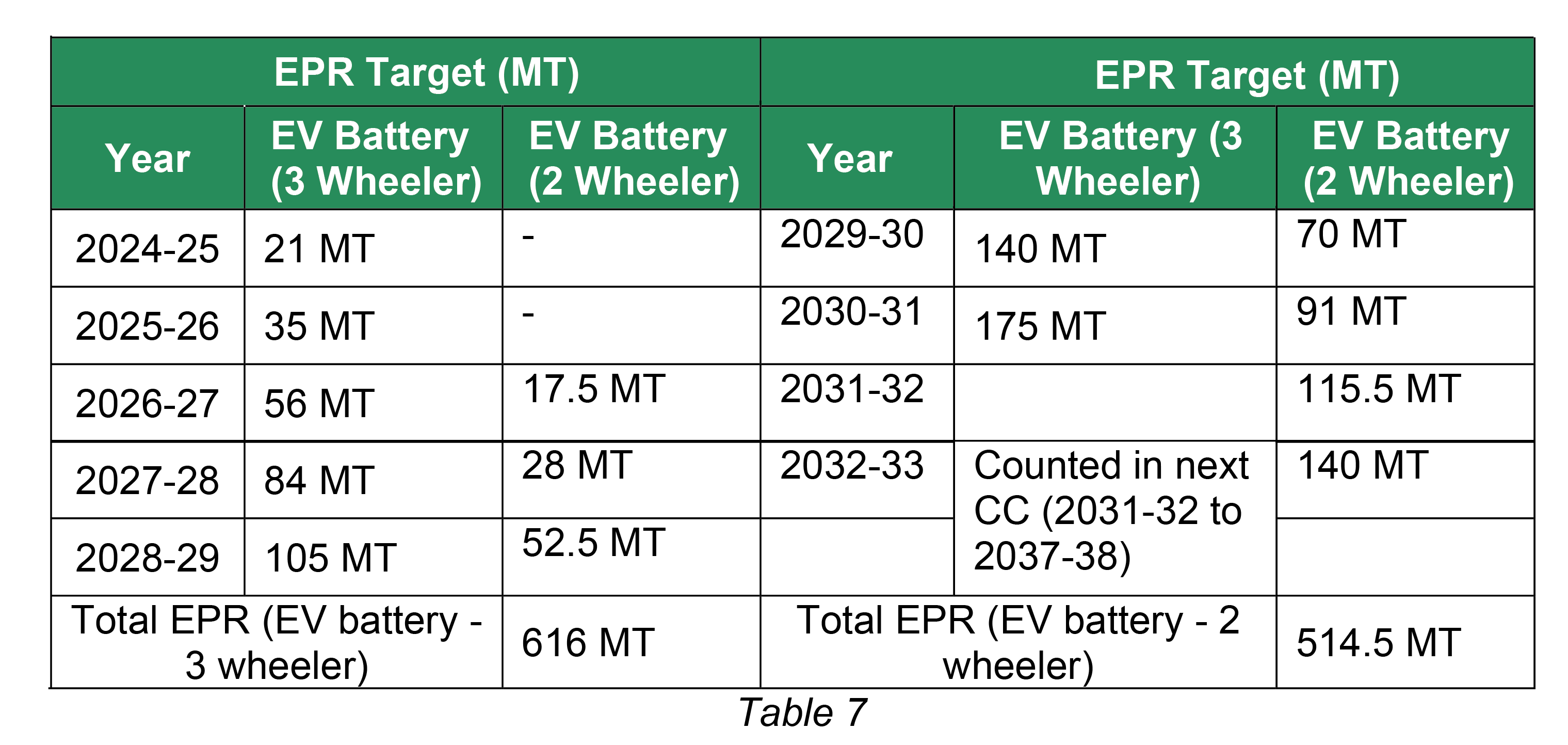
Total year wise EPR target fulfilled by “PQR” = 616 MT
The EPR target of complete 7 yr. CC (2024-25 to 2030-31) = 2120 MT
The balance EPR liability of ‘PQR’ for the said CC = 2120 – 616 = 1504 MT
However, as per clause (x) of Schedule II of the said rules, 60% of the average quantity of the battery sold per year during the compliance cycle (2024-25 to 2030-31) could be carried forward to the next compliance cycle (2031-32 to 2037-38)
Average quantity of battery sold /yr. during 2024-25 to 2030-31 = 2120/7 = ~303 MT
Hence, carry forward quantity = 60% * 303 = ~182 MT
Therefore, the balance mandatory EPR liability of ‘PQR’ for “EV batteries in 3 wheelers” during the compliance cycle of 2024-25 to 2030-31 = 1504 – 182 = 1322 MT
(b) As per clause (xi) of Schedule II of Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, the EPR liability of “PQR” for “EV battery for 2 wheelers” would be as given in table 6 below;

Total year wise EPR target fulfilled by “PQR” = 514.5 MT
The EPR target of complete 7 yr. CC (2024-25 to 2030-31) = 2150 MT
The balance EPR liability of ‘PQR’ for the said CC = 2150 – 514.5 = 1635.5 MT
However, as per the clause (xi) of Schedule II of the said rules, 60% of the average quantity of the battery sold per year during the compliance cycle (2026-27 to 2032-33) could be carried forward to the next compliance cycle (2033-34 to 2039-40)
Average quantity of battery sold /yr. during 2026-27 to 2032-33 = 2150/7 = ~307 MT
Hence, carry forward quantity = 60% * 307 = ~184 MT
Therefore, the balance mandatory EPR liability of ‘PQR’ for “EV batteries in 2 wheelers” during the compliance cycle of 2026-27 to 2032-33 = 1635.5 – 184 = 1451.5 MT
(c) Total year wise and cumulative EPR liability for the company “PQR” (for both kind of batteries sold) is presented in table 7 below;
• The balance mandatory EPR liability of company ‘PQR’ for “EV batteries in 3 wheelers” during the compliance cycle of 2024-25 to 2030-31 = 1322 MT
• The balance mandatory EPR liability of company ‘PQR’ for “EV batteries in 2 wheelers” during the compliance cycle of 2026-27 to 2032-33 = 1451.5 MT

 Previous Post
Previous Post